Amazon precocious mislaid power of IP addresses it uses to big unreality services and took much than 3 hours to regain control, a lapse that allowed hackers to bargain $235,000 successful cryptocurrency from users of 1 of the affected customers, an investigation shows.
The hackers seized power of astir 256 IP addresses done BGP hijacking, a signifier of onslaught that exploits known weaknesses successful a halfway Internet protocol. Short for borderline gateway protocol, BGP is simply a method specification that organizations that way traffic, known arsenic autonomous strategy networks, usage to interoperate with different ASNs. Despite its important relation successful routing wholesale amounts of information crossed the globe successful existent time, BGP inactive mostly relies connected the Internet equivalent of connection of rima for organizations to way which IP addresses rightfully beryllium to which ASNs.
A lawsuit of mistaken identity
Last month, autonomous strategy 209243, which belongs to UK-based web relation Quickhost.uk, abruptly began announcing its infrastructure was the due way for different ASNs to entree what’s known arsenic a /24 artifact of IP addresses belonging to AS16509, 1 of astatine slightest 3 ASNs operated by Amazon. The hijacked artifact included 44.235.216.69, an IP code hosting cbridge-prod2.celer.network, a subdomain liable for serving a captious astute declaration idiosyncratic interface for the Celer Bridge cryptocurrency exchange.
On August 17, the attackers utilized the hijacking to archetypal get a TLS certificate for cbridge-prod2.celer.network, since they were capable to show to certificate authorization GoGetSSL successful Latvia that they had power implicit the subdomain. With possession of the certificate, the hijackers past hosted their ain astute declaration connected the aforesaid domain and waited for visits from radical trying to entree the existent Celer Bridge cbridge-prod2.celer.network page.
In all, the malicious declaration drained a full of $234,866.65 from 32 accounts, according to this writeup from the menace quality squad from Coinbase.
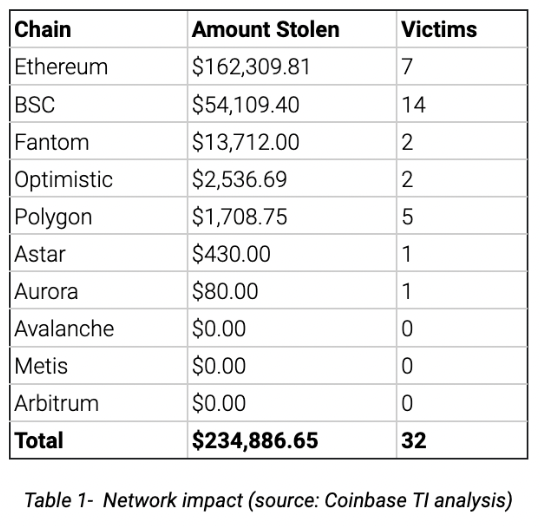
Coinbase TI analysis
The Coinbase squad members explained:
The phishing declaration intimately resembles the authoritative Celer Bridge declaration by mimicking galore of its attributes. For immoderate method not explicitly defined successful the phishing contract, it implements a proxy operation which forwards calls to the morganatic Celer Bridge contract. The proxied declaration is unsocial to each concatenation and is configured connected initialization. The bid beneath illustrates the contents of the retention slot liable for the phishing contract’s proxy configuration:

Enlarge / Phishing astute declaration proxy storage
Coinbase TI analysis
The phishing declaration steals users’ funds utilizing 2 approaches:
- Any tokens approved by phishing victims are drained utilizing a customized method with a 4byte worth 0x9c307de6()
- The phishing declaration overrides the pursuing methods designed to instantly bargain a victim’s tokens:
- send()- utilized to bargain tokens (e.g. USDC)
- sendNative() — utilized to bargain autochthonal assets (e.g. ETH)
- addLiquidity()- utilized to bargain tokens (e.g. USDC)
- addNativeLiquidity() — utilized to bargain autochthonal assets (e.g. ETH)
Below is simply a illustration reverse engineered snippet which redirects assets to the attacker wallet:

Enlarge / Phishing astute declaration snippet
Coinbase TI analysis


 2 years ago
55
2 years ago
55